Proven Strategies for Success in Urban Gardening
Maximize Soil Health in Urban Gardens

To ensure successful urban gardening, maintaining healthy soil is paramount, particularly in densely populated areas where space is limited. Urban environments often encounter distinct challenges, including compacted soil and insufficient organic matter. Mastering soil management techniques can lead to remarkable improvements in gardening outcomes. Begin by conducting a soil test to evaluate pH levels and nutrient content, then enrich your soil with compost or organic fertilizers as needed. Regularly incorporating organic materials enhances soil structure, which is essential for optimal drainage and aeration, both critical for thriving plant growth.
Key strategies for maintaining soil health in urban gardens include:
- Composting: Establish compost bins or participate in community composting programs to transform organic waste into nutrient-rich amendments.
- Mulching: Apply mulch to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
- Crop rotation: Rotate plant families each season to prevent nutrient depletion.
- Raised beds: Opt for raised beds to enhance soil structure and drainage, particularly in compact urban soils.
- Soil amendments: Regularly add organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to enrich soil health.
- Cover cropping: Utilize cover crops during off-seasons to protect soil from erosion and boost fertility.
- Microbial inoculants: Introduce beneficial microorganisms to enhance soil health and stimulate plant growth.
- Minimal tillage: Reduce disturbance to conserve soil integrity and health.
By implementing these techniques, urban gardeners can cultivate resilient and healthy plants, even in the most confined spaces.
Effective Watering Strategies for Thriving Urban Gardens
Implementing efficient watering practices is essential for urban gardening, especially with a growing focus on water conservation. By employing innovative watering methods, you can enhance water efficiency, improve plant vitality, and support sustainable practices in urban landscapes. Utilizing drip irrigation systems or soaker hoses enables targeted watering, significantly reducing evaporation and runoff. Additionally, developing smart watering schedules based on weather patterns ensures that your plants receive sufficient hydration while minimizing unnecessary water waste.
To promote responsible watering in urban gardens, consider the following techniques:
- Drip irrigation: Set up a drip system to consistently provide moisture directly to plant roots.
- Rain barrels: Collect rainwater to lessen reliance on municipal water sources.
- Soil moisture sensors: Implement sensors to track when plants need watering, preventing over- or under-watering.
- Water during cooler times: Water in the early morning or late evening to reduce evaporation and allow plants to absorb moisture efficiently.
- Hydroponics: Explore hydroponic systems that minimize water usage while maximizing plant growth.
- Mulching: Employ mulch to retain soil moisture and decrease the frequency of watering.
- Self-watering containers: Use containers that automatically maintain moisture levels.
- Companion planting: Group plants with similar water needs to enhance watering efficiency.
By adopting these approaches, urban gardeners can ensure their plants flourish while conserving vital resources.
Mastering the Essentials of Container Gardening
Container gardening has become a fantastic solution for urban residents dealing with limited space or poor soil quality. It offers flexibility in selecting plants and design, allowing a wide variety of species to thrive in small areas. The core of successful container gardening begins with choosing appropriate containers that ensure adequate drainage and are appropriately sized for your selected plants. Opt for pots made from materials such as clay, plastic, or wood, each offering distinct benefits.
Effectively managing a container garden involves understanding several key elements:
- Drainage: Ensure containers are equipped with drainage holes to prevent waterlogging and root rot.
- Soil mix: Utilize a premium potting mix specifically formulated for container gardening.
- Fertilization: Regularly nourish container plants with a balanced fertilizer to promote vigorous growth.
- Placement: Position containers in well-lit areas that meet the specific sunlight requirements of the plants.
- Watering: Frequently check moisture levels; container plants typically require more water than ground-planted ones.
- Rotation: Rotate plants or rearrange containers to maximize exposure to sunlight.
- Seasonal considerations: Be mindful of seasonal changes; some containers may need to be relocated indoors during winter.
- Companion planting: Combine plants that offer mutual benefits to enhance growth and pest resistance.
By mastering these essential principles of container gardening, urban gardeners can create vibrant green spaces, even in the most constrained environments.
Expert Tips for Thriving in Urban Gardening
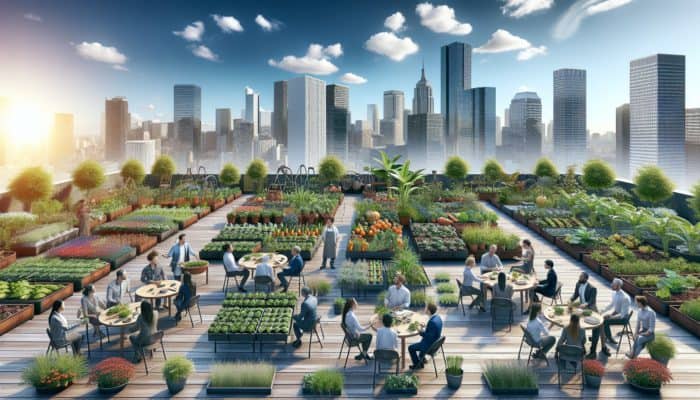

Showcasing Inspiring Urban Gardening Success Stories
Across the globe, there are numerous inspiring success stories in urban gardening that highlight the creativity and perseverance of urban gardeners. Cities such as Havana in Cuba, Detroit in the USA, and Tokyo in Japan exemplify how innovation and determination can lead to thriving urban gardens, even in challenging circumstances. These initiatives not only enhance access to fresh produce but also promote community spirit and encourage self-sufficiency.
Common factors contributing to the success of these urban gardens include:
- Community involvement: Engaging local residents ensures widespread support and active participation.
- Adaptability: Successful gardens adjust to their unique urban environments and specific challenges.
- Education: Providing training and resources empowers community members to participate in gardening endeavors.
- Collaboration: Partnering with local organizations increases resource availability and expertise.
- Resourcefulness: Utilizing recycled materials and local resources minimizes costs and environmental impact.
- Long-term vision: Establishing sustainable practices is crucial for the longevity of urban gardening projects.
- Innovative design: Creative use of space and gardening techniques maximizes productivity.
- Advocacy: Promoting the benefits of urban gardening garners public and governmental support.
These real-world examples demonstrate that successful urban gardening projects can have a profound impact on communities, transforming bustling cities into flourishing green spaces.
Practical Steps to Launch Your Urban Garden
Starting an urban gardening project may seem intimidating; however, breaking it down into manageable steps makes it accessible for anyone interested in growing plants in a city. Begin by evaluating your available space, whether it’s a balcony, rooftop, or small yard. Understanding your surroundings—such as sunlight exposure, wind conditions, and water access—will guide your plant selections.
Here’s a straightforward guide to kick-starting your urban garden:
- Define your goals: Determine what you want to grow—herbs, vegetables, or flowers—and clarify your primary objectives.
- Choose your space: Identify suitable locations that receive adequate sunlight and have accessible water sources.
- Select containers: If using pots, choose sizes that accommodate the plants you intend to grow.
- Gather supplies: Collect soil, seeds, or seedlings, along with essential tools like shovels, watering cans, and gloves.
- Prepare the site: Clear the area of debris, rocks, and weeds to create an optimal planting environment.
- Plant your seeds: Follow specific planting guidelines for each plant type, including depth and spacing requirements.
- Water and care: Establish a watering routine and closely monitor plant health, adjusting care as necessary.
- Engage with your community: Share progress and seek advice from fellow urban gardeners to build connections.
By following these actionable steps, you can embark on your urban gardening journey with confidence, cultivating a thriving green space that benefits both you and your community.
Addressing Common Urban Gardening Challenges with Expert Solutions
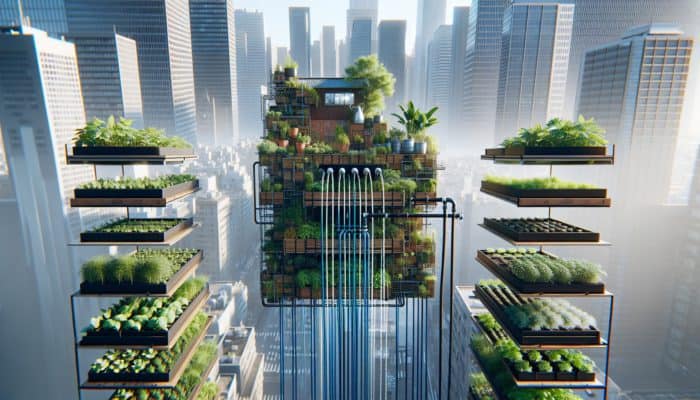

Urban gardening presents unique challenges that can deter many aspiring gardeners. Common issues include limited space, poor soil quality, water restrictions, and pest management problems. Recognizing these challenges allows gardeners to devise strategic solutions that lead to rewarding gardening experiences.
Addressing these obstacles begins with awareness and proactive planning. For instance, limited space can be effectively managed through vertical gardening techniques, optimizing every available inch. Poor soil quality may necessitate intensive soil management practices, such as raised beds or container gardening, to enhance soil conditions. Water restrictions can be mitigated by adopting efficient watering methods, such as drip irrigation or rainwater harvesting.
Challenges frequently encountered by urban gardeners include:
- Insufficient sunlight: Analyze sun patterns and select plants suitable for partial shade or consider implementing grow lights.
- Limited space: Incorporate vertical gardening or rooftop gardens to maximize available growing areas.
- Pest pressures: Employ integrated pest management strategies that utilize natural predators and organic repellents.
- Soil contamination: Conduct soil tests and consider raised beds filled with clean soil for safety.
- Access to water: Utilize rainwater harvesting systems and efficient irrigation methods to alleviate scarcity.
- Community regulations: Familiarize yourself with local gardening laws and restrictions to ensure compliance.
- Seasonal limitations: Use cold frames or greenhouses to extend the growing season in urban areas.
- Resource availability: Connect with local gardening networks for shared tools, knowledge, and resources.
By acknowledging these challenges and applying expert recommendations, urban gardeners can transform potential setbacks into opportunities for innovation and success.
Exploring the Community Impact of Urban Gardening
Urban gardening greatly influences not only individual benefits but also plays a vital role in strengthening local communities. Urban gardens serve as vibrant green spaces that encourage community engagement, provide educational opportunities, and promote social cohesion. They transform neglected areas into thriving ecosystems, significantly enhancing residents’ quality of life.
Urban gardens act as social hubs where community members interact, exchange knowledge, and cultivate relationships. These spaces often serve as educational platforms, teaching individuals about sustainable practices, nutrition, and food security. Additionally, they offer access to fresh produce, which is critical in food deserts—urban regions lacking affordable, nutritious food.
Key impacts of urban gardening on communities include:
- Community empowerment: Urban gardens equip residents with the knowledge and resources to take control of their food systems.
- Social connections: Gardens foster relationships among neighbors, strengthening community bonds.
- Educational opportunities: They serve as outdoor classrooms for schools, encouraging hands-on learning about the environment and nutrition.
- Improved well-being: Access to green spaces contributes to mental health and encourages physical activity.
- Food security: Urban gardens provide fresh produce, reducing reliance on grocery stores.
- Environmental benefits: They enhance local biodiversity and encourage sustainable practices within urban settings.
- Economic opportunities: Urban gardens can generate local jobs and stimulate the economy through produce sales.
- Artistic expression: Many gardens incorporate art, enriching the visual landscape of urban areas.
By harnessing the potential of urban gardening, communities can create resilient, sustainable environments that benefit all residents.
Innovative Techniques and Technologies in Urban Gardening
Innovation in urban gardening is crucial for overcoming the challenges posed by limited space and resources. A variety of cutting-edge techniques and technologies have emerged, enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of urban gardening practices. These advancements facilitate increased productivity, reduced environmental impact, and greater accessibility.
One notable innovative technique is vertical gardening, which utilizes vertical surfaces to grow plants in urban environments. This method optimizes limited ground space and enhances aesthetics, contributing to urban beautification. Hydroponics and aquaponics systems provide soil-less growing methods that consume significantly less water than traditional gardening, making them ideal for areas facing water scarcity.
Additional innovative approaches include:
- Smart gardening technology: Use applications and devices to monitor plant health, soil moisture, and weather conditions.
- Community-supported agriculture (CSA): Involve residents through subscription models that deliver fresh produce directly from urban farms.
- Permaculture principles: Implement sustainable design practices that integrate with natural ecosystems to create self-sustaining gardens.
- Mobile gardening units: Utilize portable gardens or planters that can be easily relocated to adapt to changing sunlight or other environmental conditions.
- Urban beekeeping: Incorporate beekeeping into urban gardens to support pollination and enhance local biodiversity.
- Soil-less growing systems: Explore aeroponics and other techniques that require minimal water and space.
- Green roofs: Establish gardens on rooftops to improve insulation and reduce stormwater runoff.
- Neighborhood seed banks: Create local repositories for seeds to promote biodiversity and resilience in urban gardening.
By embracing these innovative techniques and technologies, urban gardeners can significantly enhance their gardening experiences and contribute to the development of sustainable urban environments.
The Health Benefits of Urban Gardening
Physical Health Advantages of Gardening
Engaging in urban gardening offers a multitude of physical health benefits that extend beyond simply enjoying fresh produce. Gardening tasks, such as digging, planting, and weeding, serve as excellent forms of exercise that can enhance overall fitness and well-being. Regular involvement in these activities can lower the risk of chronic diseases, improve cardiovascular health, and aid in weight management.
Gardening promotes physical activity that encompasses strength, flexibility, and endurance. These activities can be especially beneficial for individuals seeking enjoyable methods to incorporate movement into their daily routines. Additionally, the process of growing food can inspire individuals to adopt healthier eating habits, as having readily available homegrown produce encourages a greater intake of fruits and vegetables.
Key physical health benefits of gardening include:
- Increased physical activity: Gardening tasks provide an enjoyable means of incorporating exercise into your daily life.
- Improved cardiovascular health: Regular gardening is associated with lower blood pressure and enhanced heart health.
- Muscle strengthening: Activities like lifting, digging, and bending build muscle strength and enhance overall fitness.
- Enhanced motor skills: Gardening requires coordination and fine motor skills, promoting physical dexterity.
- Weight management: Routine gardening helps burn calories and maintain a healthy weight.
- Exposure to fresh air: Spending time outdoors improves respiratory health and boosts vitamin D levels.
- Reduced risk of chronic illness: Active gardening can lower the likelihood of developing obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
- Healthy eating habits: Growing your own fruits and vegetables encourages a nutrient-rich diet.
Urban gardening serves as a multi-faceted approach to enhancing physical health while fostering a sustainable lifestyle.
Mental Health Benefits of Access to Green Spaces
Connecting with nature yields substantial psychological benefits, particularly in urban settings where green spaces are limited. Urban gardening provides a unique opportunity to engage with nature, promoting mental well-being and alleviating stress. Research indicates that spending time in green areas can help reduce anxiety, enhance feelings of happiness, and improve overall life satisfaction.
Gardening can serve as a mindfulness practice, allowing individuals to focus on the present while nurturing plants. The act of caring for living things fosters a sense of achievement and purpose, positively impacting mental health. Furthermore, building community connections through gardening can reduce feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Key mental health benefits of urban gardening include:
- Stress reduction: Gardening activities can lower cortisol levels, contributing to decreased stress and anxiety.
- Enhanced mood: Interacting with plants and nature increases feelings of happiness and contentment.
- Mindfulness: Engaging in gardening promotes a state of mindfulness, enhancing present-moment awareness.
- Social connections: Community gardening nurtures relationships, diminishing feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Sense of achievement: Successfully growing plants provides a tangible sense of accomplishment, boosting self-esteem.
- Creativity boost: Garden design and planning stimulate creativity and problem-solving abilities.
- Nature exposure: Access to green spaces is associated with lower rates of depression and anxiety.
- Improved cognitive function: Time spent in nature can enhance focus and cognitive abilities.
By incorporating urban gardening into your lifestyle, you can enjoy the mental health benefits associated with connecting with nature and fostering community ties.
Nutritional Advantages of Homegrown Produce
Urban gardening not only offers physical and mental health benefits but also enhances nutrition by providing access to fresh, homegrown produce. Cultivating fruits and vegetables at home encourages healthier eating habits and increases the intake of nutrient-rich foods. Homegrown produce often boasts superior freshness and flavor compared to store-bought alternatives, leading to greater enjoyment and satisfaction.
Furthermore, urban gardening empowers individuals to make informed choices about their food sources and dietary preferences. By growing a diverse range of plants, gardeners can tailor their gardens to meet their nutritional needs and taste preferences. This practice promotes self-sufficiency and can help mitigate food insecurity within urban populations.
Key nutritional benefits of urban gardening include:
- Access to fresh produce: Homegrown fruits and vegetables provide superior freshness and nutrient density.
- Increased variety: Cultivating a diverse array of plants fosters a varied diet rich in essential nutrients.
- Reduced reliance on processed foods: Gardening encourages the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods.
- Organic options: Home gardens allow for the growth of food without synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
- Flavor enhancement: Freshly harvested vegetables often taste better than store-bought counterparts.
- Education on nutrition: Gardening imparts valuable lessons about healthy eating and food preparation.
- Cost savings: Growing your own produce can lower grocery bills and enhance food security.
- Empowerment: Taking control of your food sources fosters a sense of self-sufficiency and personal agency.
By embracing urban gardening, individuals can reap the nutritional benefits of fresh produce while cultivating a deeper connection to their food sources.
Implementing Sustainable Practices in Urban Gardening
Composting Techniques for City Dwellers
Composting is a foundational practice for sustainable urban gardening, enabling city residents to recycle organic waste and enrich their soil. In densely populated areas, where waste disposal can be challenging, composting transforms kitchen scraps and yard waste into valuable nutrients for plants. Effectively implementing composting methods can significantly improve soil health and contribute to waste reduction efforts.
Starting a compost bin in an urban environment involves selecting suitable materials and maintaining a balanced compost pile. Ideal compost ingredients consist of green materials (nitrogen-rich items like fruit scraps and grass clippings) and brown materials (carbon-rich items such as dried leaves and cardboard). Achieving the right balance between these components is essential for successful composting.
Key composting strategies for city dwellers include:
- Bin selection: Choose a compost bin that fits your space—options include tumblers, stackable bins, or DIY containers.
- Layering: Alternate layers of green and brown materials to maintain a healthy balance.
- Aeration: Regularly turn the compost to aerate and expedite the decomposition process.
- Moisture control: Keep the compost pile moist but not overly wet to encourage microbial activity.
- Monitoring temperature: Maintain temperatures between 130°F and 160°F (54-71°C) for efficient compost breakdown.
- Worm Composting: Utilize vermicomposting with worms to speed up the composting process and produce nutrient-rich worm castings.
- Community composting: Join or start a community composting initiative to share resources and collectively reduce waste.
- Finished compost usage: Use the finished compost to enrich your garden soil, enhancing plant health and productivity.
By adopting composting techniques, urban gardeners can significantly decrease waste while enhancing the sustainability of their gardening practices.
Rainwater Harvesting for Urban Gardens
Rainwater harvesting represents a sustainable approach that allows urban gardeners to collect and utilize rainwater for irrigation. This practice reduces dependency on municipal water supplies and contributes to resource conservation, making it particularly important in cities facing increasing water scarcity. Implementing rainwater harvesting systems can be simple or complex, depending on available resources and space.
To effectively harvest rainwater, urban gardeners can install systems such as rain barrels or cisterns. These setups capture runoff from rooftops, providing a sustainable and free water source for irrigation. Utilizing rainwater in your garden not only promotes conservation but also benefits overall plant health, as rainwater is typically free of the chemicals found in tap water.
Key steps for rainwater harvesting in urban gardens include:
- Barrel selection: Choose a rain barrel that suits your garden size and water requirements.
- Location: Position the barrel beneath a downspout to maximize water collection.
- First flush diverters: Install a diverter to prevent the initial contaminated runoff from entering the barrel.
- Filtration: Use mesh screens to filter out debris and insects from the harvested water.
- Storage capacity: Ensure the barrel has enough capacity to meet your garden’s watering needs.
- Watering methods: Use collected rainwater for irrigation, either manually or through drip systems.
- Seasonal considerations: Prepare your rainwater system for winter by draining barrels to prevent freezing.
- Community engagement: Share knowledge about rainwater harvesting with neighbors to promote broader water conservation initiatives.
Through rainwater harvesting, urban gardeners can create sustainable watering systems that support healthy plant growth while conserving this vital resource.
Eco-Friendly Pest Control Techniques
Managing pests in urban gardens can be challenging, but adopting eco-friendly pest control methods ensures plant health without harming the environment. Chemical pesticides can negatively impact local ecosystems, making it essential to explore sustainable alternatives. Eco-friendly pest management focuses on prevention, natural deterrents, and biological controls to effectively manage pests.
Preventive strategies include selecting pest-resistant plant varieties and maintaining healthy soil to promote vigorous plant growth. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies involve monitoring pest populations and applying targeted interventions when necessary. Introducing beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, can also help control pest populations naturally.
Key eco-friendly pest management techniques include:
- Companion planting: Pair plants that naturally repel pests when planted alongside vulnerable species.
- Neem oil: Utilize this natural pesticide derived from the neem tree to manage various pests.
- Insecticidal soap: Apply soap sprays to suffocate soft-bodied pests like aphids and spider mites.
- Beneficial insects: Introduce predatory insects to naturally manage pest populations without chemicals.
- Physical barriers: Use row covers or nets to physically block pests from reaching plants.
- DIY traps: Create traps from household items to capture specific pests like fruit flies or slugs.
- Herbal repellents: Use homemade sprays from herbs such as mint or garlic to deter unwanted pests.
- Healthy plant care: Maintain proper watering and fertilization to enhance plant resilience against pests.
By implementing these eco-friendly pest management strategies, urban gardeners can protect their plants while supporting a healthy and balanced ecosystem.
Vertical Gardening as a Solution for Space Constraints
Vertical gardening offers an innovative solution for urban gardeners facing space limitations, enabling them to maximize their growing area while beautifying their environment. By utilizing vertical surfaces, gardeners can cultivate a variety of plants—from vegetables to ornamental flowers—without requiring extensive ground space. This technique not only optimizes growing conditions but also contributes to urban beautification and sustainable practices.
To create a vertical garden, various structures and systems can be employed, including wall planters, trellises, and vertical frames. These systems can be adapted to fit different spaces, from compact balconies to larger community gardens. Successful vertical gardening relies on selecting appropriate plants that thrive in these conditions and ensuring they receive adequate light and water.
Innovative vertical gardening solutions include:
- Wall planters: Use wall-mounted planters to create green walls that enhance your property’s visual appeal.
- Living fences: Construct fences or screens from climbing plants to improve privacy and aesthetics.
- Trellises: Install trellises for climbing plants—perfect for peas, beans, and cucumbers.
- Pallet gardens: Repurpose wooden pallets for vertical planting, creating artistic garden displays.
- Hanging pots: Suspend pots from ceilings or hooks to effectively utilize overhead space.
- Hydroponic towers: Implement vertical hydroponic systems for efficient, soilless growing.
- Stackable planters: Use stackable containers to create multi-tiered gardens in limited spaces.
- Gutter gardens: Repurpose old gutters to create long, narrow planting containers mounted on walls or fences.
By embracing vertical gardening techniques, urban gardeners can grow a diverse array of plants while maximizing limited space and contributing to urban greening initiatives.
Incorporating Native Plants for Biodiversity in Urban Gardens
Integrating native plants into urban gardens represents a sustainable practice that significantly boosts biodiversity and ecological health. Native plants are well-suited to local conditions, requiring less water, fertilizer, and maintenance compared to non-native varieties. By utilizing native flora, urban gardeners can create resilient ecosystems that support local wildlife, including pollinators and beneficial insects.
Moreover, native plants often contribute to improving soil health and preventing erosion, making them valuable assets in urban landscapes. Selecting plants that thrive naturally in the local environment ensures that gardens remain vibrant, productive, and sustainable over time.
Key benefits of incorporating native plants into urban gardens include:
- Biodiversity enhancement: Native plants support local wildlife, promoting healthier ecosystems.
- Low maintenance: These plants require less water and care, making them ideal for busy urban gardeners.
- Soil health improvement: Native species often enhance soil quality through deep root systems.
- Climate adaptation: Native plants are naturally resilient to local climate conditions, minimizing the need for intervention.
- Pest resistance: Native plants are generally less susceptible to pests and diseases than non-native species.
- Cultural significance: Many native plants hold cultural importance and can connect communities to their heritage.
- Water conservation: Native plants usually need less irrigation, making them suitable for areas with limited water resources.
- Seasonal interest: Native plants often provide visual appeal throughout different seasons, showcasing their natural beauty.
By prioritizing native plants in urban gardening, gardeners can contribute to sustainable practices that benefit both the environment and their communities.
Choosing the Best Plants for Urban Gardening
Selecting Ideal Vegetables for Urban Gardens
Choosing the right vegetables for urban gardens is crucial for ensuring successful growth and plentiful harvests. Factors such as space limitations, climate conditions, and sunlight exposure significantly influence which vegetables are best suited for urban settings. Opting for varieties that thrive in containers or small garden beds can maximize productivity and minimize challenges.
Popular vegetable choices for urban gardening include fast-growing and high-yielding options that provide ample rewards for limited space. Vegetables like tomatoes and peppers are particularly well-suited for containers and can thrive in small areas with adequate sunlight.
Recommended vegetables for city gardens include:
- Tomatoes: A favorite choice, tomatoes flourish in containers and yield abundant crops.
- Radishes: Quick-growing and requiring minimal space, radishes can be harvested in as little as three weeks.
- Lettuce: Leafy greens like lettuce are perfect for compact spaces and can be harvested continuously.
- Herbs: Such as basil, parsley, and cilantro thrive in containers, enhancing culinary dishes.
- Peppers: Both sweet and hot varieties grow well in pots, offering a range of flavors.
- Green beans: Climbing varieties can effectively utilize vertical space and yield plentiful harvests.
- Carrots: Suitable for containers, carrots grow deep in the soil, making them ideal for urban settings.
- Spinach: A nutritious choice that flourishes in cooler temperatures and can be cultivated in limited space.
By thoughtfully selecting vegetables for urban gardens, gardeners can optimize their growing conditions and enjoy a productive and rewarding gardening experience.
Choosing Herbs That Thrive in Urban Environments
Herbs are an excellent choice for urban gardening due to their versatility, compact growth habit, and culinary benefits. Growing herbs in urban settings allows gardeners to enjoy fresh flavors while enhancing the visual appeal of their gardens. Many herbs flourish in containers or small garden beds, making them ideal for confined spaces.
The ability to regularly harvest herbs encourages gardeners to incorporate more fresh ingredients into their meals, promoting healthier eating habits. Furthermore, many herbs attract pollinators, contributing to biodiversity in urban ecosystems.
Recommended herbs for urban gardening include:
- Basil: A versatile herb that thrives in warm weather and can be grown in containers or garden beds.
- Mint: A hardy herb that grows easily, though it may require containment to prevent spreading.
- Parsley: A biennial herb that flourishes in various conditions and elevates culinary dishes.
- Thyme: This low-growing herb prefers well-drained soil and can be cultivated in small spaces.
- Cilantro: A fast-growing herb that can be harvested multiple times throughout its growing season.
- Chives: A perennial herb that adds flavor to dishes and grows well in containers.
- Oregano: A drought-tolerant herb that thrives in sunny locations and requires minimal maintenance.
- Sage: A fragrant herb that flourishes in containers and enhances the flavor of various dishes.
By cultivating these herbs in urban gardens, gardeners can enjoy the benefits of fresh, flavorful ingredients while enhancing biodiversity and sustainability.
Enhancing Urban Spaces with Ornamental Plants
In addition to functional plants, incorporating ornamental plants into urban gardens not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also contributes to the overall greening of urban environments. Ornamental plants can beautify small spaces, provide shade, and create a welcoming atmosphere for both residents and visitors. Selecting the right ornamental plants is crucial to ensure they thrive in urban settings and complement the surrounding landscape.
When choosing ornamental plants, consider factors such as climate, light conditions, and maintenance requirements. Plants well-suited for urban environments typically possess traits like drought resistance, pollution tolerance, and pest resilience.
Recommended ornamental plants for urban beautification include:
- Marigolds: Bright, cheerful flowers that are easy to grow and attract beneficial insects.
- Lavender: A fragrant perennial that adds beauty and attracts pollinators.
- Hydrangeas: These flowering shrubs provide stunning blooms and thrive in a variety of conditions.
- Succulents: Low-maintenance plants that introduce unique textures and colors to urban gardens.
- Hostas: Shade-tolerant perennials that offer lush foliage and require minimal care.
- Ornamental grasses: These plants add movement and texture to gardens while being low-maintenance.
- Roses: Classic, fragrant flowers that can flourish in urban gardens with the right care.
- Ferns: Shade-loving plants that provide lush greenery and thrive in urban environments.
By thoughtfully incorporating ornamental plants into urban gardens, gardeners can contribute to urban beautification while enhancing their connection to nature.
Research-Backed Benefits of Urban Gardening Survival
Assessing the Impact of Urban Gardening on Community Cohesion
Urban gardening significantly influences community cohesion, fostering connections among residents and encouraging collective efforts toward sustainability. Gardening initiatives create opportunities for individuals to collaborate, share resources, and build friendships, ultimately strengthening the social fabric of neighborhoods. These community-driven projects often lead to increased engagement, empowerment, and a sense of belonging.
Research shows that urban gardens can serve as social hubs where community members come together to work, learn, and celebrate. They provide platforms for shared experiences, skill-building, and knowledge exchange, which are vital for cultivating strong relationships across diverse populations.
Key impacts of urban gardening on community cohesion include:
- Building relationships: Gardening promotes social interaction and helps individuals connect across cultural boundaries.
- Shared goals: Collaborating on gardening projects fosters a sense of purpose and unity.
- Resource sharing: Community gardens encourage the exchange of tools, seeds, and expertise, alleviating individual burdens.
- Empowerment: Residents gain skills and confidence through gardening, fostering leadership within the community.
- Healthier neighborhoods: Access to fresh produce enhances community health, leading to a shared interest in well-being.
- Environmental stewardship: Engaging in gardening encourages responsible environmental practices among community members.
- Increased civic engagement: Community gardens often spur greater involvement in local governance and decision-making.
- Celebrating diversity: Shared gardening experiences highlight cultural diversity and promote inclusivity.
By harnessing the power of urban gardening to enhance community cohesion, residents can create vibrant, resilient neighborhoods that thrive together.
Real-Life Examples of Urban Gardening’s Environmental Benefits
Urban gardening initiatives yield significant environmental benefits, contributing to the sustainability and ecological health of cities worldwide. These projects enhance biodiversity, improve air quality, and mitigate the urban heat island effect. By transforming vacant lots and rooftop spaces into green oases, urban gardens promote a healthier environment for both humans and wildlife.
Cities such as Detroit in Michigan and Melbourne in Australia have successfully implemented urban gardening projects that prioritize environmental sustainability. These initiatives not only provide fresh produce but also restore ecosystems and create habitats for wildlife.
Key environmental benefits of urban gardening include:
- Biodiversity enhancement: Urban gardens create habitats for pollinators and other beneficial organisms.
- Air quality improvement: Plants filter pollutants and enhance air quality in densely populated areas.
- Stormwater management: Gardens absorb rainwater, reducing runoff and minimizing flooding risks.
- Carbon sequestration: Urban gardens help capture and store carbon dioxide, mitigating climate change effects.
- Temperature regulation: Green spaces lower temperatures, reducing the urban heat island effect and energy consumption.
- Soil health restoration: Urban gardening practices improve soil quality and prevent erosion.
- Community resilience: Gardens enhance food security and promote self-sufficiency in urban areas.
- Waste reduction: Composting and recycling practices in urban gardens decrease landfill waste.
These real-world examples illustrate how urban gardening initiatives contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly urban landscape.
Measuring the Success of Urban Gardening Initiatives
Evaluating the success of urban gardening initiatives is essential for demonstrating their impact and sustainability. By tracking various metrics, gardeners and community organizers can assess progress, identify areas for improvement, and advocate for ongoing support. Establishing clear goals and benchmarks is crucial for effective evaluation.
Actionable steps for measuring success in urban gardening initiatives include:
- Set specific goals: Define measurable objectives, such as increased production, community engagement, or educational outreach.
- Collect data: Regularly gather information on plant growth, harvest yields, and participant involvement.
- Surveys and feedback: Conduct surveys among participants and community members to evaluate satisfaction and gather suggestions.
- Monitor environmental impact: Track changes in biodiversity, soil health, and air quality resulting from gardening initiatives.
- Document progress: Keep records of gardening activities, challenges faced, and lessons learned throughout the growing season.
- Community participation: Involve community members in evaluation processes to ensure diverse perspectives are considered.
- Celebrate successes: Highlight achievements and milestones to inspire continued participation and support.
- Adjust strategies: Use collected data to inform decisions and refine gardening practices for future success.
By implementing these actionable steps, urban gardeners can effectively measure and communicate the success of their initiatives, fostering ongoing community engagement and support.
Exploring the Psychological Benefits of Urban Gardening for Individuals
Urban gardening provides numerous psychological benefits that can enhance individual well-being and quality of life. Engaging in gardening activities offers a therapeutic outlet, enabling individuals to connect with nature and experience the calming effects of nurturing plants. Research suggests that spending time in green spaces can alleviate stress, promote relaxation, and improve overall mental well-being.
Gardening fosters a sense of achievement and purpose as individuals witness the results of their efforts. This tangible connection to nature can elevate feelings of self-worth and promote mindfulness, allowing individuals to focus on the present moment and escape daily stresses.
Key psychological benefits of urban gardening include:
- Stress relief: Gardening activities can lower stress levels and promote relaxation through physical engagement.
- Mindfulness: Connecting with plants encourages present-moment awareness, fostering a sense of calm.
- Improved mood: Interaction with nature and observing plant growth can lead to increased happiness and satisfaction.
- Social interaction: Community gardening nurtures relationships, reducing feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Creative expression: Gardening provides opportunities for creativity and self-expression through design and plant selection.
- Enhanced self-esteem: Successfully nurturing plants boosts confidence and provides a sense of accomplishment.
- Connection to nature: Spending time in green spaces fosters appreciation for the environment and encourages sustainability.
- Resilience building: Overcoming gardening challenges can enhance problem-solving skills and personal resilience.
By embracing urban gardening, individuals can cultivate not only plants but also improved mental well-being and emotional health.
Evaluating the Economic Advantages of Urban Gardening in Urban Settings
Urban gardening initiatives offer significant economic benefits that can benefit both individuals and communities. These projects can lead to cost savings, job creation, and increased property values, creating a positive ripple effect within urban areas. By investing in urban gardens, cities can promote economic resilience and sustainability, while also enhancing the quality of life for their residents.
One of the most tangible economic benefits of urban gardening is the reduction in food costs. Growing fresh produce at home decreases reliance on grocery stores and allows individuals to save money on groceries. Furthermore, community gardens can provide access to affordable, nutritious food for low-income neighborhoods, addressing food insecurity.
Key economic advantages of urban gardening include:
- Cost savings: Growing your own food lowers grocery expenses and enhances food security.
- Job creation: Urban gardening initiatives can generate jobs in landscaping, gardening education, and food production.
- Increased property values: Well-maintained gardens enhance neighborhood aesthetics and can raise property values.
- Local economies: Urban gardens can stimulate local economies through farmers’ markets and community-supported agriculture.
- Green jobs: Promoting gardening initiatives can lead to the development of green jobs in urban agriculture.
- Community engagement: Urban gardens foster entrepreneurship and skill development among community members.
- Environmental cost savings: Increased green space can reduce urban infrastructure costs, including those associated with stormwater management.
- Investment in public health: Improved access to fresh produce contributes to better health outcomes, reducing healthcare costs.
By exploring the economic advantages of urban gardening, communities can recognize the potential for sustainable growth and enhanced individual prosperity.
Maximizing Space in Urban Gardening
Space-Efficient Vertical Gardening Techniques
Maximizing available space is vital for successful urban gardening, especially in densely populated areas. Vertical gardening presents an innovative solution, allowing gardeners to utilize vertical surfaces for plant growth. By implementing vertical gardening techniques, urban gardeners can create lush, productive environments while enhancing the aesthetics of their surroundings.
To effectively implement vertical gardening, consider various structures and systems that support plant growth while maximizing limited ground space. These solutions are particularly advantageous for small balconies, courtyards, or community garden plots.
Practical vertical gardening solutions include:
- Wall-mounted planters: Use wall planters to create green walls that occupy minimal ground space.
- Trellises and arbors: Install these structures to support climbing plants and utilize vertical height.
- Hanging baskets: Suspend baskets from ceilings or hooks to optimize overhead space and add visual interest.
- Living fences: Use climbing plants to create natural barriers that enhance privacy and aesthetics.
- Stacked planters: Utilize tiered systems to facilitate multiple levels of planting in small areas.
- Gutter gardens: Repurpose old gutters as planters mounted vertically to grow herbs or small vegetables.
- Vertical hydroponic systems: Implement hydroponic towers that use less water and soil while maximizing growing space.
- Pallet gardens: Use wooden pallets to create vertical planting surfaces for herbs and flowers.
By adopting these vertical gardening solutions, urban gardeners can effectively maximize their growing spaces and cultivate a diverse array of plants.
Utilizing Rooftop Gardening for Space Maximization
Rooftop gardening offers a unique opportunity for urban gardeners to maximize space while contributing to green infrastructure. Rooftop gardens can transform unused or underutilized spaces into productive, vibrant environments that benefit both the gardener and the surrounding community. However, rooftop gardening requires careful planning and consideration of structural aspects to ensure safety and sustainability.
Key techniques for successful rooftop gardening include assessing the roof’s load-bearing capacity, selecting suitable plants, and implementing an efficient watering system. It’s crucial to create a well-draining garden system that minimizes water retention and prevents structural damage.
Practical rooftop gardening techniques include:
- Weight considerations: Ensure the rooftop can bear the weight of soil, plants, and water.
- Container gardening: Use lightweight containers to reduce overall weight while maximizing planting options.
- Drainage systems: Implement proper drainage solutions to prevent water accumulation and structural damage.
- Soil selection: Use lightweight, high-quality potting mixes designed for rooftop gardens.
- Microclimate assessment: Consider wind exposure and sunlight when placing plants to optimize growth conditions.
- Watering systems: Utilize drip irrigation or self-watering systems to efficiently manage water usage.
- Access pathways: Design pathways to ensure easy access for maintenance and harvesting without damaging plants.
- Permaculture principles: Implement sustainable practices that enhance biodiversity and promote environmental health.
By employing these rooftop gardening techniques, urban gardeners can effectively transform rooftops into productive green spaces that benefit both individuals and the community.
Creative Solutions for Small Space Gardening
Innovative approaches to small-space gardening are essential for urban gardeners aiming to maximize productivity in confined areas. Creative strategies can significantly enhance the ability to grow a variety of plants, even in the tiniest of spaces. These innovations often focus on utilizing vertical structures, efficient container designs, and novel growing techniques.
Emphasizing space-saving techniques enables urban gardeners to cultivate fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants within limited areas such as balconies, patios, or small yards. Many of these innovations promote sustainability and encourage a diverse range of plants.
Innovative methods for small space gardening include:
- Container gardening: Utilize various container types, including vertical planters, to maximize space and grow multiple plants.
- Stackable planters: Employ tiered planter systems to create multi-level gardens in small areas.
- Square foot gardening: Use grid techniques to efficiently plan and organize planting, optimizing every square foot.
- Hydroponics or aquaponics: Implement soil-less growing methods that conserve space and water while maximizing yield.
- Intercropping: Combine compatible plants in the same space to utilize resources efficiently and improve yields.
- Vertical trellising: Use vertical supports for climbing plants to conserve ground space and boost productivity.
- Recycled materials: Repurpose items like old pallets or crates as planting containers to minimize waste and cost.
- Community gardens: Participate in shared gardening spaces that allow for the cultivation of diverse plants without requiring extensive individual space.
By leveraging these small space gardening innovations, urban gardeners can create thriving gardens that contribute to sustainability and enhance the beauty of urban landscapes.
Effective Strategies for Flourishing in Urban Gardening
Analyzing the Economic Advantages of Urban Gardening
Urban gardening presents numerous economic benefits that extend beyond individual gardening efforts, contributing to community prosperity and resilience. By promoting local food production, urban gardens can lower food costs and improve access to fresh produce. This, in turn, enhances food security and supports the overall health of urban populations.
Moreover, urban gardening initiatives can create job opportunities in gardening, landscaping, and sustainable agriculture, stimulating local economies. Community gardens often serve as platforms for entrepreneurial ventures, such as farmers’ markets or small-scale food businesses, further boosting economic growth.
Key economic benefits of urban gardening include:
- Local food production: Urban gardens provide fresh produce, reducing reliance on distant suppliers and promoting local economies.
- Job creation: Gardening initiatives can generate jobs in urban agriculture, education, and related fields.
- Cost savings: Growing food at home lowers grocery bills and food expenses for urban residents.
- Increased property values: Well-maintained gardens contribute to neighborhood aesthetics and can raise property values.
- Community development: Urban gardens promote collaboration and resource sharing among residents, strengthening community ties.
- Promoting entrepreneurship: Gardens can serve as incubators for local food businesses and innovative agricultural practices.
- Public health cost savings: Improved access to fresh produce can lead to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
- Sustainable practices: Urban gardening promotes environmental sustainability, leading to long-term economic benefits for communities.
By recognizing the economic benefits of urban gardening, communities can see the potential for growth, resilience, and enhanced overall well-being.
Educational Opportunities through Urban Gardening
Integrating urban gardening into educational settings offers valuable learning experiences that transcend traditional classroom boundaries. Schools and educational institutions worldwide have embraced gardening initiatives to educate students about sustainability, nutrition, and environmental stewardship. These programs foster hands-on learning, encouraging students to develop a deeper understanding of where their food comes from and the importance of caring for the environment.
Real-world examples of successful urban gardening initiatives in educational settings highlight their positive impact on student engagement and community involvement. Schools that incorporate gardening into their curricula often experience improved academic performance, heightened interest in science, and enhanced social skills.
Key examples of urban gardening in educational settings include:
- School gardens: Many schools have established gardens to teach students about food production, ecology, and nutrition.
- Community partnerships: Collaborations with local organizations provide resources and expertise for school gardening initiatives.
- Curriculum integration: Schools integrate gardening into subjects like science, math, and health, promoting interdisciplinary learning.
- Student-led initiatives: Empowering students to lead gardening projects fosters leadership skills and a sense of responsibility.
- Garden-to-table programs: Schools incorporate harvested produce into cafeterias, promoting awareness of healthy eating.
- Environmental education: School gardens serve as outdoor classrooms for teaching sustainability and environmental science.
- Parent and community involvement: Engaging families in gardening activities strengthens community ties and support.
- Workshops and events: Schools host workshops to educate families and the community about gardening and nutrition.
By incorporating urban gardening into educational settings, schools can create enriching experiences that foster a love for nature and healthy living.
Actionable Steps for Integrating Urban Gardening into Daily Life
Incorporating urban gardening into daily life can enhance personal well-being, promote sustainability, and foster community engagement. By making small changes and integrating gardening practices into everyday routines, individuals can reap the numerous benefits of cultivating plants and growing their own food.
Actionable steps for integrating urban gardening into daily life include:
- Start small: Begin with a few pots or a small garden bed to ease into gardening without overwhelming yourself.
- Commit to daily time: Dedicate a few minutes each day to garden maintenance, such as watering or weeding.
- Plan your garden: Develop a planting plan that considers available space, sunlight, and desired plants.
- Join a community garden: Connect with local gardeners to share resources, knowledge, and support.
- Educate yourself: Attend workshops or read books on gardening techniques and best practices to expand your knowledge.
- Involve family and friends: Engage loved ones in gardening activities to foster a sense of community and collaboration.
- Use social media: Share your gardening experiences online to inspire and connect with others.
- Celebrate successes: Acknowledge achievements, whether small or large, to maintain motivation and enthusiasm for gardening.
By following these actionable steps, individuals can seamlessly incorporate urban gardening into their daily lives, creating a positive impact on their health and the environment.
Discussing the Environmental Impact of Urban Gardening
Urban gardening has a profound environmental impact, contributing to sustainability and ecological health in urban areas. By transforming vacant lots and underutilized spaces into green oases, urban gardens enhance biodiversity, improve air quality, and mitigate the effects of climate change. These gardens not only provide fresh produce but also create habitats for wildlife, promoting a sense of stewardship for the environment.
Research indicates that urban gardens can significantly reduce the urban heat island effect by providing shade and increasing evapotranspiration. This cooling effect can help lower energy consumption and improve overall urban livability. Additionally, green spaces have been linked to improved mental health and well-being among residents, creating a positive feedback loop that fosters community engagement and environmental responsibility.
Key environmental impacts of urban gardening include:
- Biodiversity enhancement: Urban gardens create habitats for pollinators, beneficial insects, and other wildlife.
- Air quality improvement: Plants help filter pollutants from the air, contributing to better air quality for urban residents.
- Stormwater management: Gardens absorb rainwater, reducing runoff and minimizing flooding risks.
- Improving soil health: Urban gardening practices enhance soil quality and contribute to local food production.
- Carbon sequestration: Urban gardens capture carbon dioxide, helping mitigate climate change.
- Temperature regulation: Green spaces help cool urban areas, reducing reliance on air conditioning.
- Waste reduction: Composting and recycling practices in urban gardens decrease landfill waste and pollution.
- Community resilience: Urban gardening promotes self-sufficiency and local food production, enhancing community resilience to economic challenges.
By recognizing the environmental impact of urban gardening, communities can leverage these benefits to create sustainable and thriving urban landscapes.
Highlighting the Community-Building Aspects of Urban Gardening
Urban gardening serves as a powerful tool for community building, fostering connections among residents and promoting collective action toward sustainability. By creating shared green spaces, urban gardens encourage collaboration, social interaction, and a sense of belonging. These communal efforts can lead to strengthened neighborhood ties, increased civic engagement, and a shared commitment to environmental stewardship.
Gardening initiatives often unite individuals from diverse backgrounds and cultures, promoting inclusivity and understanding. Collaborative gardening projects foster teamwork and encourage sharing of skills, resources, and knowledge. Additionally, urban gardens can act as venues for community events, workshops, and celebrations, further enhancing social connections.
Key community-building aspects of urban gardening include:
- Collaboration: Urban gardens encourage teamwork among residents, promoting a sense of shared purpose.
- Social interaction: Gardening projects create opportunities for individuals to connect and build relationships.
- Community leadership: Residents often take on leadership roles in gardening initiatives, fostering a sense of empowerment and community engagement.
- Inclusivity: Urban gardens welcome individuals from diverse backgrounds, highlighting cultural richness.
- Resource sharing: Community gardens facilitate the exchange of tools, seeds, and knowledge among gardeners.
- Event organization: Urban gardens serve as venues for community gatherings, workshops, and social events.
- Collective learning: Residents learn from each other, sharing gardening techniques and sustainability practices.
- Celebration of diversity: Community gardens often reflect the cultural diversity of the neighborhood through plant selections and gardening practices.
By harnessing the community-building potential of urban gardening, neighborhoods can cultivate stronger, more resilient communities that thrive together.
Encouraging Community Involvement in Urban Gardening
Building Urban Gardening Networks for Collaboration
Establishing urban gardening networks is vital for connecting aspiring gardeners, sharing resources, and building community resilience. These networks provide platforms for collaboration and knowledge exchange, fostering a sense of belonging among urban gardeners. By connecting with local organizations, community groups, and gardening enthusiasts, individuals can access valuable support and resources that enhance their gardening experiences.
To build effective urban gardening networks, consider the following strategies:
- Join local gardening groups: Participate in community gardening organizations to meet fellow gardeners and share experiences.
- Organize workshops: Host gardening workshops to educate community members about gardening techniques and sustainability practices.
- Participate in events: Attend local gardening events and fairs to connect with other gardeners and learn from experts.
- Share resources: Develop a resource-sharing system that allows gardeners to exchange tools, seeds, and knowledge.
- Utilize social media: Create online platforms or groups to facilitate communication and support among urban gardeners.
- Engage youth: Encourage young people to participate in gardening initiatives, fostering a new generation of gardeners.
- Collaborate with local businesses: Partner with local shops to support gardening projects and promote community initiatives.
- Advocate for policies: Work with local officials to promote policies that support urban gardening and green spaces.
By establishing urban gardening networks, communities can cultivate a supportive environment that encourages collaboration, knowledge sharing, and collective growth.
The post Urban Gardening Survival: Thrive in Cities appeared first on Survival Bite.
The Article Urban Gardening Survival Tips for Thriving in Cities Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com


No responses yet